Difference between Clustered Index Scan and Index Scan in SQL Server
1.Clustered Index Scan
✅ What it is:
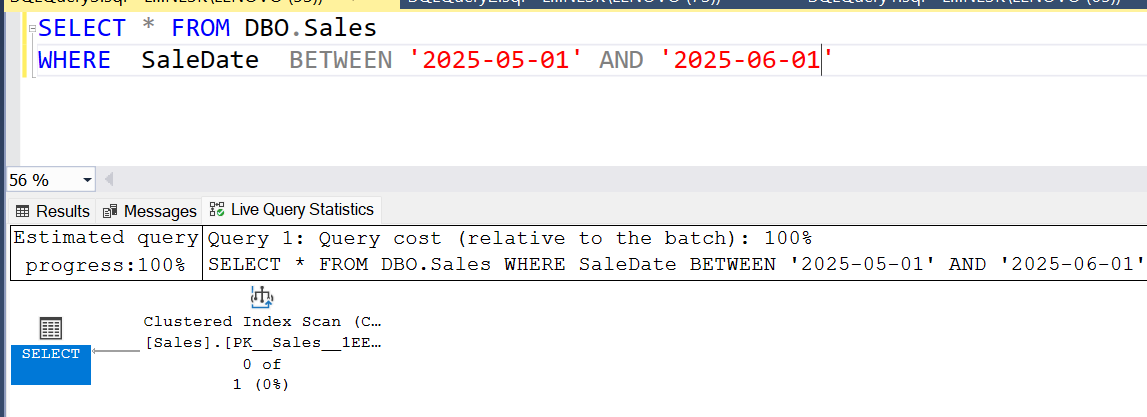
- A Clustered Index Scan means SQL Server is scanning every row of the entire table, essentially performing a "table scan" because the clustered index is the table itself.
📌 When it happens:
- No WHERE clause or very broad filter (low selectivity).
- Join/filter columns aren’t indexed selectively.
- Query needs most or all columns (covering queries).
🧠 Performance Insight:
- Can be expensive for large tables.
- Usually appears when SQL Server can’t seek and needs to read all data.
Example:
Table:
CREATE TABLE dbo.Sales
(
SaleID INT NOT NULL IDENTITY,
SaleDate DATE NOT NULL,
Quantity INT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (SaleID)
)
Query:
SELECT * FROM dbo.SalesWHERE SaleDate BETWEEN '2025-02-04' AND '2025-02-10'
2. Index Scan (Non-Clustered)
✅ What it is:
- A Non-Clustered Index Scan scans all rows in a specific non-clustered index( not the full table)
📌 When it happens:
- The query filters on a column included in a non-clustered index, but can’t use a seek.
🧠 Performance Insight:
- Faster than scanning the whole table if only a few indexed columns are needed.
- Less I/O than clustered scan when index is narrow and well-designed.


Comments
Post a Comment